The objective of this article is to demonstrate how to use rFAMS to calculate yield based on a slot length limit with multiple values of conditional fishing and conditional natural mortality. Separate conditional fishing mortality for fish under slot, within slot, and above slot must be specified. This allows the user to investigate a protective slot where fish are protected from harvest within a length range and an inverted slot where small fish under the slot and large fish over the slot limit are protected while harvesting is allowed within the slot limit.
Build a life history parameter list
The first step for using any of the rFAMS simulation models is to create an object with life history parameters using the makeLH() function. The makeLH() function creates a list of the life history parameters needed. Including, the initial number of recruits, maximum age of fish in your population, von Bertalanffy growth model parameters (, , and ), and parameters from the log10-transformed weight length model (alpha and beta). By default, the makeLH() returns a list. Growth length-weight model paramaters can be generated from functions in the FSA package. The example below uses the following life history parameters:
- NO is the initial number of recruits, set to 100.
- tmax is the maximum age in the population in years, set to 15.
- Linf is the point estimate of asymptotic mean length from the von Bertalanffy growth model, set to 592mm.
- K (upper case) is the point estimate of the Brody growth coefficient from the von Bertalanffy growth model, set to 0.20.
- t0 is the point estimate of the x-intercept (i.e., theoretical age at a mean length of 0) from the von Bertalanffy growth model, set to -0.3.
- LWalpha is the point estimate of alpha from the length-weight regression on the log10 scale, set to -5.528.
- LWbeta is the point estimate of beta from the length-weight regression on the log10 scale, set to 3.273.
# create life history parameter object
LH <- makeLH(N0=100,tmax=15,Linf=592,K=0.20,t0=-0.3,LWalpha=-5.528,LWbeta=3.273)Estimate yield for one minimum length limit and variable conditional fishing and conditional natural mortality.
The function yprBH_SlotLL() function is used when yield is estimated with a slot limit and conditional fishing mortality is specified below, within, and above the slot. This function requires a recruitment length recruitmentTL (i.e., the length where fish are susceptible to harvest, this is NOT the lower slot limit); lower slot limit lowerSL; upper slot limit upperSL; conditional fishing mortality under the slot limit but above recruitment length cfunder; conditional fishing mortality within the slot limit cfin; conditional fishing mortality above the slot limit cfabove; specified range of conditional natural mortality by setting the minimum cmmin, maximum cmmax, and increment cminc; set any length of interest to monitor loi; and the life history parameters lhparams.
rFAMS includes a function est_natmort() to estimate instantaneous natural mortality (M) and conditional natural mortality (cm) using parameters specified in the life history parameter object. See the FSA package for other methods of calculating M and cm. To generate the range and average M and cm using rFAMS:
est_natmort(LH, incl.avg = TRUE)
#> method M cm givens
#> 1 HoenigNLS 0.4100226 0.33636478 tmax=15
#> 2 HoenigO 0.2954353 0.25579246 tmax=15
#> 3 HoenigO2 0.2963197 0.25645032 tmax=15
#> 4 HoenigLM 0.3612696 0.30320890 tmax=15
#> 5 HewittHoenig 0.2813333 0.24522330 tmax=15
#> 6 tmax1 0.3406000 0.28865661 tmax=15
#> 7 PaulyLNoT 0.3308050 0.28165477 K=0.2, Linf=59.2
#> 8 K1 0.3384000 0.28708993 K=0.2
#> 9 K2 0.4080000 0.33502112 K=0.2
#> 10 HamelCope 0.3600000 0.30232367 tmax=15
#> 11 JensenK1 0.3000000 0.25918178 K=0.2
#> 12 JensenK2 0.5040000 0.39589062 K=0.2
#> 13 AlversonCarney 0.2821182 0.24581544 tmax=15, K=0.2
#> 14 ChenWatanabe 0.1018740 0.09685666 tmax=15, K=0.2, t0=-0.3
#> 15 AVERAGE 0.3292984 0.27782360Once you have decided the range of cf and cm and decided what minimum length limit to consider, you can now proceed to estimating yield. The following example uses the life history object created above with a minimum length limit of 200mm, cf from 0.1 to 0.9 with increments of 0.1, cm from 0.1 to 0.9 with increments of 0.1, monitors lengths of 200, 250, 300, and 350mm.
Res_1 <- yprBH_SlotLL(recruitmentTL=200,lowerSL=250,upperSL=325, #Set recruitment and slot limit length
cfunder=0.25,cfin=0.6,cfabove=0.15, #Set cf under, in, and above slot limit
cmmin=0.1,cmmax=0.9,cminc=0.1, #creates vector of cm values
loi=c(200,250,300,350,450,550), #sets lengths of interest to monitor
lhparms=LH) #Specifies life history parametersThe output object will be a data.frame with the following calculated values:
- cm A numeric representing conditional natural mortality
- yieldTotal is the calculated total yield
- nharvTotal is the calculated total number of harvested fish
- ndieTotal is the calculated total number of fish that die of natural death
- yieldUnder is the calculated yield under the slot limit
- yieldIn is the calculated yied within the slot limit
- yieldAbove is the calculated yield above the slot limit
- exploitationUnder is the exploitation rate under the slot limit
- exploitationIn is the exploitation rate within the slot limit
- exploitationAbove is the exploitation rate above the slot limit
- nharvestUnder is the number of harvested fish under the slot limit
- nharvestIn is the number of harvested fish within the slot limit
- nharvestAbove is the number of harvested fish above the slot limit
- n0die is the number of fish that die of natural death before entering the fishery at a minimum length
- ndieUnder is the number of fish that die of natural death under the slot limit
- ndieIn is the number of fish that die of natural deaths within the slot limit
- ndieAbove is the number of fish that die of natural deaths above the slot limit
- avglenUnder is the average length of fish harvested under the slot limit
- avglenIn is the average length of fish harvested within the slot limit
- avglenAbove is the average length of fish harvested above the slot limit
- avgwtUnder is the average weight of fish harvested under the slot limit
- avgwtIn is the average weight of fish harvested within the slot limit
- avgwtAbove is the average weight of fish harvested above the slot limit
- trUnder is the time for a fish to recruit to a minimum length limit (i.e., time to enter fishery)
- trIn is the time for a fish to recruit to a lower length limit of the slot limit
- trOver is the time for a fish to recruit to a upper length limit of the slot limit
- nrUnder is the number of fish at time trUnder (time they become harvestable size under the slot limit)
- nrIn is the number of fish at time trIn (time they reach the lower slot limit size)
- nrAbove is the number of fish at time trAbove (time they reach the upper slot limit size)
- FUnder is the estimated instantaneous rate of fishing mortality under the slot limit
- FIn is the estimated instantaneous rate of fishing mortality within the slot limit
- FAbove is the estimated instantaneous rate of fishing mortality above the slot limit
- MUnder is the estimated instantaneous rate of natural mortality under the slot limit
- MIn is the estimated instantaneous rate of natural mortality within the slot limit
- MAbove is the estimated instantaneous rate of natural mortality above the slot limit
- ZUnder is the estimated instantaneous rate of total mortality under the slot limit
- ZIn is the estimated instantaneous rate of total mortality within the slot limit
- ZAbove is the estimated instantaneous rate of total mortality above the slot limit
- SUnder is the estimated total survival under the slot limit
- SIn is the estimated total survival within the slot limit
- SAbove is the estimated total survival above the slot limit
- cfUnder A numeric representing conditional fishing mortality
- cfIn A numeric representing conditional fishing mortality
- cfOver A numeric representing conditional fishing mortality
- recruitmentTL A numeric representing the minimum length limit for recruiting to the fishery in mm.
- lowerSL A numeric representing the length of the lower slot limit in mm.
- upperSL A numeric representing the length of the upper slot limit in mm.
- nAtxxx is the number that reach the length of interest supplied. There will be one column for each length of interest.
For convenience the data.frame also contains the model input values (cf derived from cfUnder, cfIn, and cfOver; recruitmentTL; lowerSL; upperSL; cm derived from cmmin, cmmax, and cminc; N0; Linf; K; t0; LWalpha; LWbeta; and tmax).
View the first few rows of the output
head(Res_1)
#> yieldTotal yieldUnder yieldIn yieldAbove nharvTotal ndieTotal nharvestUnder
#> 1 29156.293 2134.0226 12847.795 14174.4754 65.545400 16.65337 14.300192
#> 2 16399.451 1661.3174 9009.265 5728.8686 44.983766 22.37093 11.186560
#> 3 9587.852 1251.5389 6037.309 2299.0040 30.319080 23.01694 8.473698
#> 4 5611.796 903.2554 3813.586 894.9547 19.682869 20.98520 6.154504
#> 5 3163.191 614.9004 2223.163 325.1268 12.040623 17.45903 4.221259
#> 6 1643.192 384.7347 1154.658 103.7991 6.727817 13.18526 2.665456
#> nharvestIn nharvestAbove n0die ndieUnder ndieIn ndieAbove nrUnder
#> 1 40.888026 10.3571826 16.93639 5.237294 4.701546 6.7145292 83.06361
#> 2 28.960251 4.8369557 32.49751 8.676970 7.052667 6.6412908 67.50249
#> 3 19.625646 2.2197362 46.64404 10.505888 7.639471 4.8715819 53.35596
#> 4 12.555729 0.9726349 59.32995 10.928309 6.999731 3.0571627 40.67005
#> 5 7.428002 0.3913628 70.50022 10.170789 5.619066 1.6691717 29.49978
#> 6 3.925836 0.1365243 80.08692 8.489694 3.925836 0.7697317 19.91308
#> nrIn nrAbove trUnder trIn trOver avglenUnder avglenIn
#> 1 63.526126 17.9365533 1.761224 2.443479 3.68129 225.5013 283.1066
#> 2 47.638955 11.6260378 1.761224 2.443479 3.68129 225.1683 282.2425
#> 3 34.376376 7.1112601 1.761224 2.443479 3.68129 224.7908 281.2776
#> 4 23.587233 4.0317725 1.761224 2.443479 3.68129 224.3558 280.1859
#> 5 15.107731 2.0606627 1.761224 2.443479 3.68129 223.8426 278.9287
#> 6 8.757933 0.9062605 1.761224 2.443479 3.68129 223.2179 277.4456
#> avglenAbove avgwtUnder avgwtIn avgwtAbove nAt200 nAt250 nAt300
#> 1 443.8067 149.2303 314.2190 1368.5648 83.06361 63.526126 28.333814
#> 2 424.6353 148.5101 311.0907 1184.3955 67.50249 47.638955 19.359309
#> 3 407.5833 147.6969 307.6235 1035.7105 53.35596 34.376376 12.570645
#> 4 393.1118 146.7633 303.7327 920.1343 40.67005 23.587233 7.636027
#> 5 381.0284 145.6675 299.2950 830.7556 29.49978 15.107731 4.234615
#> 6 370.8494 144.3410 294.1178 760.2978 19.91308 8.757933 2.057926
#> nAt350 nAt450 nAt550 cm expUnder expIn expAbove
#> 1 15.7236087 7.6991996 1.506094e+00 0.1 0.2378792 0.5739983 0.14257140
#> 2 9.6183528 3.4406800 3.284670e-01 0.2 0.2252683 0.5468307 0.13484863
#> 3 5.5094637 1.3806140 5.843904e-02 0.3 0.2120703 0.5182617 0.12677377
#> 4 2.8956814 0.4811312 7.964081e-03 0.4 0.1981511 0.4879637 0.11826676
#> 5 1.3531307 0.1382899 7.540266e-04 0.5 0.1833156 0.4554588 0.10921127
#> 6 0.5332727 0.0300664 4.211329e-05 0.6 0.1672608 0.4200000 0.09942671
#> FUnder FIn FAbove MUnder MIn MAbove ZUnder
#> 1 0.2876821 0.9162907 0.1625189 0.1053605 0.1053605 0.1053605 0.3930426
#> 2 0.2876821 0.9162907 0.1625189 0.2231436 0.2231436 0.2231436 0.5108256
#> 3 0.2876821 0.9162907 0.1625189 0.3566749 0.3566749 0.3566749 0.6443570
#> 4 0.2876821 0.9162907 0.1625189 0.5108256 0.5108256 0.5108256 0.7985077
#> 5 0.2876821 0.9162907 0.1625189 0.6931472 0.6931472 0.6931472 0.9808293
#> 6 0.2876821 0.9162907 0.1625189 0.9162907 0.9162907 0.9162907 1.2039728
#> ZIn ZAbove SUnder SIn SAbove cfUnder cfIn cfOver recruitmentTL
#> 1 1.021651 0.2678794 0.675 0.36 0.765 0.25 0.6 0.15 200
#> 2 1.139434 0.3856625 0.600 0.32 0.680 0.25 0.6 0.15 200
#> 3 1.272966 0.5191939 0.525 0.28 0.595 0.25 0.6 0.15 200
#> 4 1.427116 0.6733446 0.450 0.24 0.510 0.25 0.6 0.15 200
#> 5 1.609438 0.8556661 0.375 0.20 0.425 0.25 0.6 0.15 200
#> 6 1.832581 1.0788097 0.300 0.16 0.340 0.25 0.6 0.15 200
#> lowerSL upperSL N0 Linf K t0 LWalpha LWbeta tmax
#> 1 250 325 100 592 0.2 -0.3 -5.528 3.273 15
#> 2 250 325 100 592 0.2 -0.3 -5.528 3.273 15
#> 3 250 325 100 592 0.2 -0.3 -5.528 3.273 15
#> 4 250 325 100 592 0.2 -0.3 -5.528 3.273 15
#> 5 250 325 100 592 0.2 -0.3 -5.528 3.273 15
#> 6 250 325 100 592 0.2 -0.3 -5.528 3.273 15Plot results
We will now create a series of figures to aid in interpreting the output. First, a custom theme is created to use across all plots.
# Custom theme for plots (to make look nice)
theme_FAMS <- function(...) {
theme_bw() +
theme(
panel.grid.major=element_blank(),panel.grid.minor=element_blank(),
axis.text=element_text(size=14,color="black"),
axis.title=element_text(size=16,color="black"),
axis.title.y=element_text(angle=90),
axis.line=element_line(color="black"),
panel.border=element_blank()
)
}Yield as a function of conditional natural mortality
The first figure will be a yield curve that displays the relationship between yield as a function of conditional natural mortality.
# Total Yield vs Conditional Natural Mortality (cm)
ggplot(data=Res_1,mapping=aes(x=cm,y=yieldTotal)) +
geom_point() +
geom_line() +
labs(y="Total yield (g)",x="Conditional natural mortality (cm)") +
theme_FAMS()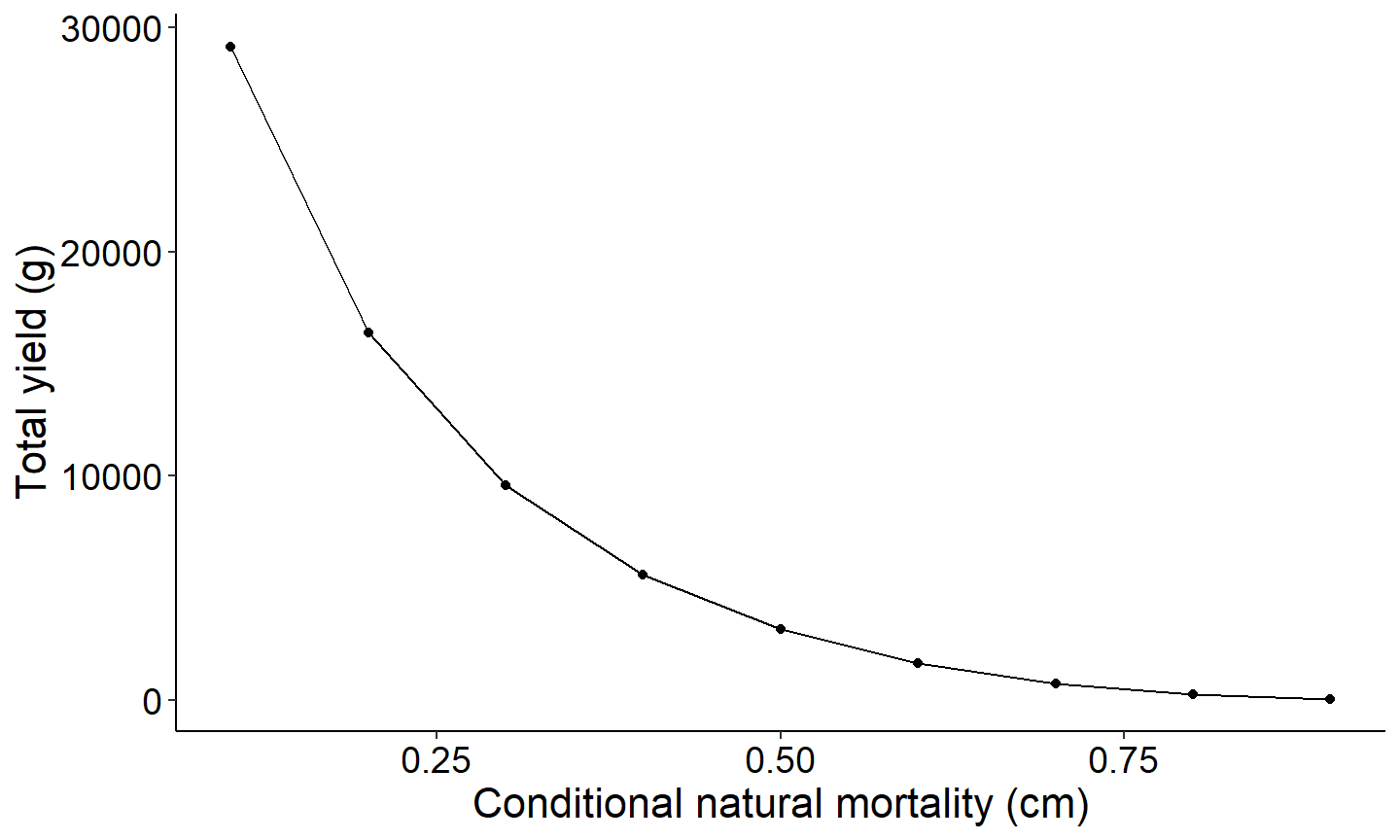
Number of fish that reach a specified size as a function of conditional natural mortality
The next figure demonstrates how to explore the number of fish reaching a specified length. This figure creates a plot showing the number of fish reaching 350mm as a function of conditional natural mortality.
#Plot number of fish reaching 350 mm as a function of cm
ggplot(data=Res_1,mapping=aes(x=cm ,y=`nAt350`)) +
geom_point() +
geom_line() +
labs(y="Number of fish at 450 mm",x="Conditional natural mortality (cm )") +
theme_FAMS()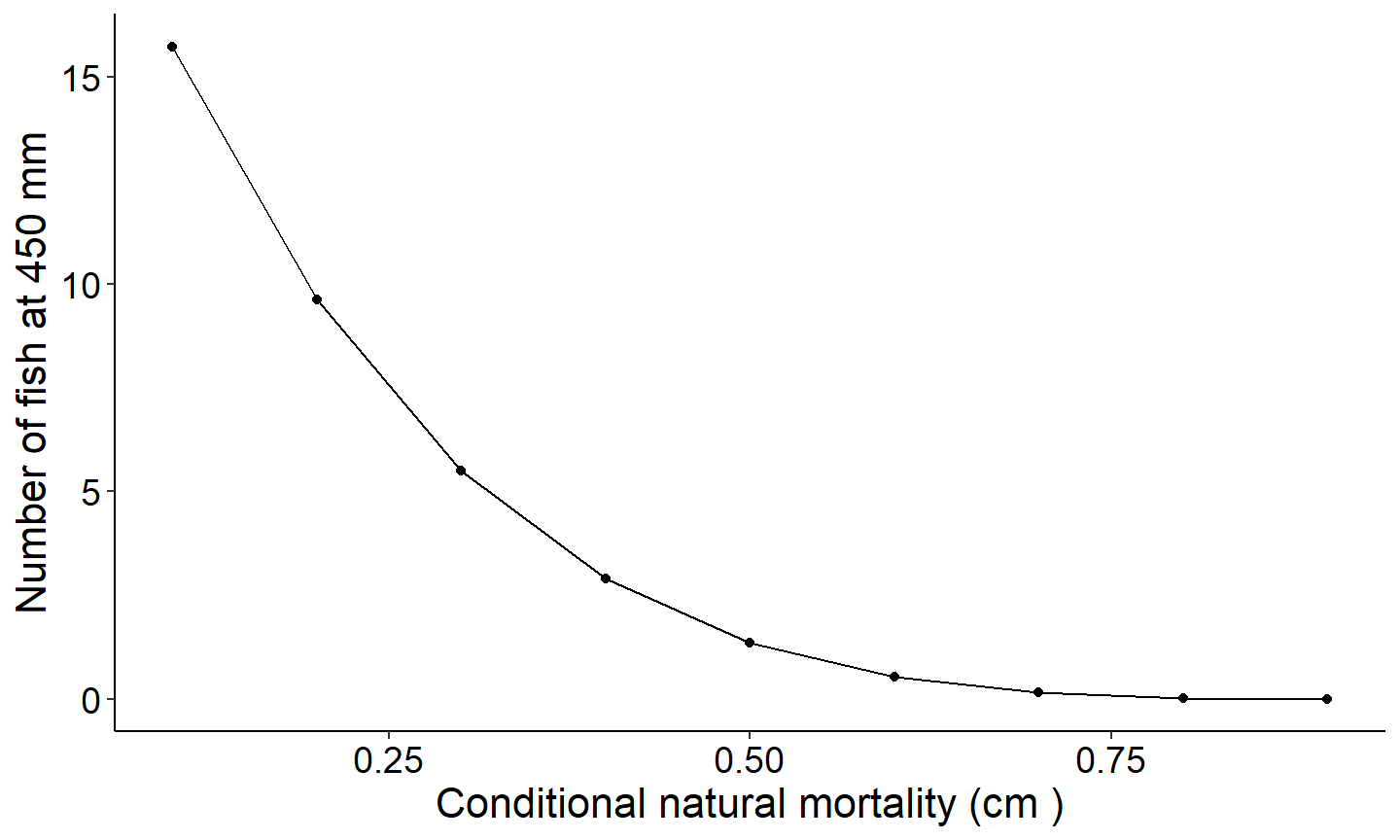
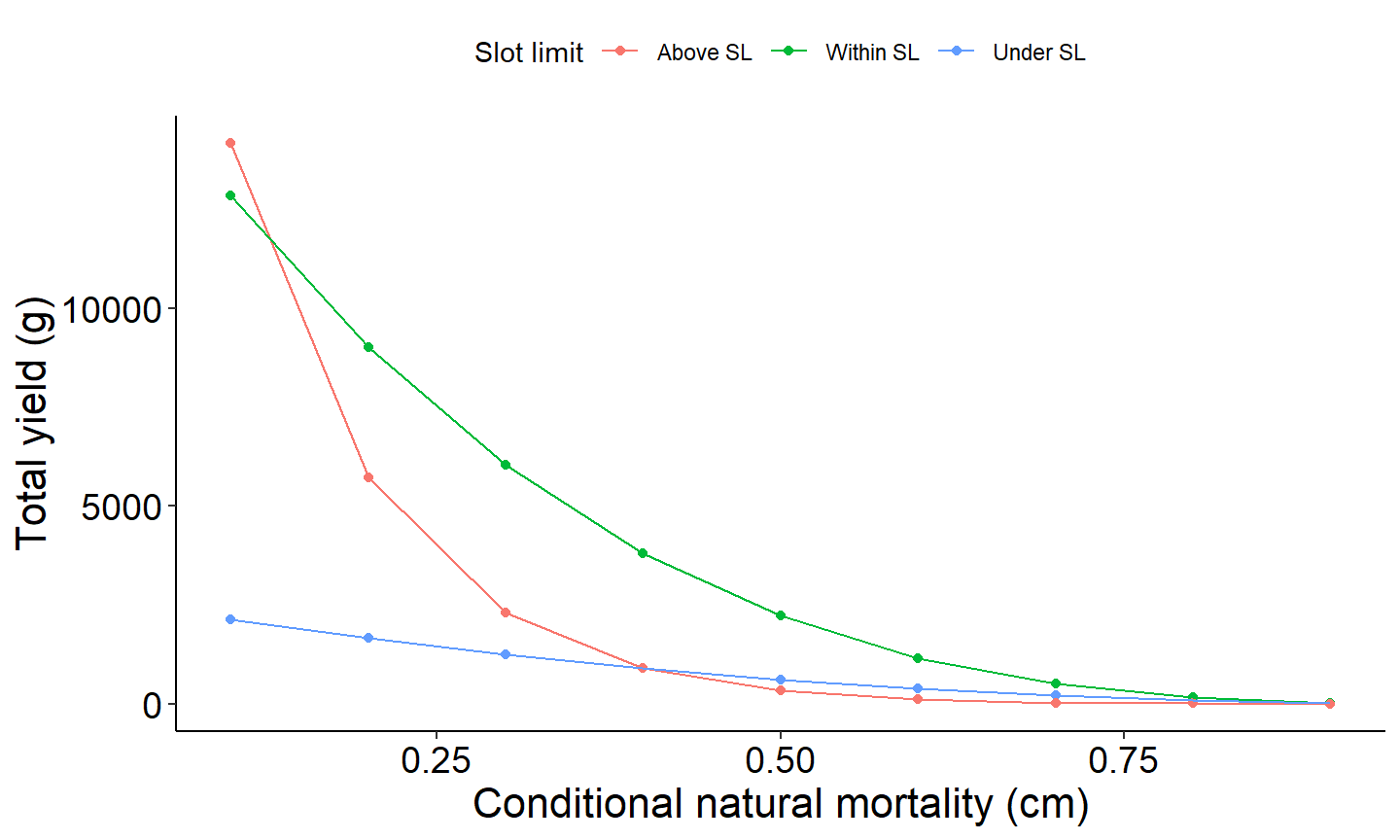
The last example figure plots yield as a function of conditional natural mortality across the three size classes; above slot limit, within slot limit, and above slot limit.
# Yield under, in, and above the slot limit vs Conditional Natural Mortality (cm)
# Select columns for plotting
plot_data <- Res_1 %>%
select(cm, yieldUnder, yieldIn, yieldAbove) %>%
pivot_longer(!cm, names_to="YieldCat",values_to="Yield")
# Generate plot
ggplot(data=plot_data,mapping=aes(x=cm,y=Yield,group=YieldCat,color=YieldCat)) +
geom_point() +
scale_color_discrete(name="Yield",labels=c("Above SL","Within SL","Under SL"))+
geom_line() +
labs(y="Total yield (g)",x="Conditional natural mortality (cm)") +
theme_FAMS() +
theme(legend.position = "top")+
guides(color=guide_legend(title="Slot limit"))